In this section, we will explore the Blender interface, which is crucial for navigating and utilizing the software effectively. Understanding the interface will help you work more efficiently and make the most of Blender's powerful features.
Key Concepts
- Workspaces
- Main Areas of the Interface
- Editors and Panels
- Customizing the Interface
Workspaces
Blender provides several predefined workspaces tailored for different tasks such as modeling, sculpting, animation, and more. Each workspace is a collection of editors arranged to facilitate specific workflows.
Common Workspaces
- Layout: General-purpose workspace for basic operations.
- Modeling: Focused on 3D modeling tasks.
- Sculpting: Optimized for sculpting workflows.
- UV Editing: For UV mapping and texture painting.
- Shading: For material and shader creation.
- Animation: For animating objects and characters.
- Rendering: For setting up and rendering scenes.
Main Areas of the Interface
Blender's interface is divided into several main areas:
- Top Bar: Contains the main menu and workspace tabs.
- 3D Viewport: The primary area where you interact with your 3D models.
- Outliner: Displays a hierarchical view of all objects in the scene.
- Properties Editor: Contains various settings and properties for the selected object.
- Timeline: Used for animation, showing keyframes and playback controls.
- Status Bar: Displays information about the current operation and system status.
Interface Layout
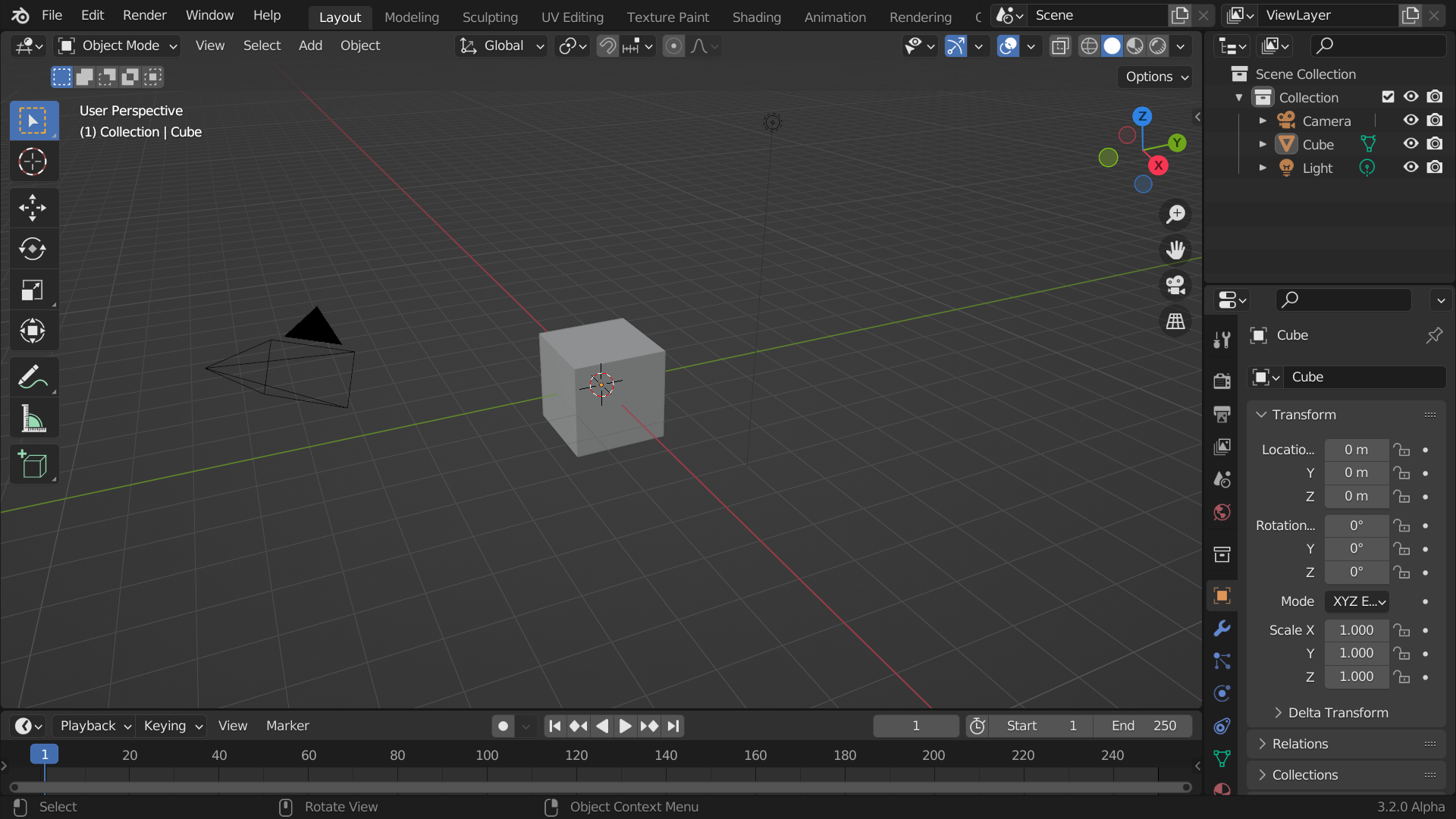
Editors and Panels
Blender's interface is composed of various editors, each serving a specific purpose. Here are some of the most commonly used editors:
3D Viewport
The 3D Viewport is where you interact with your 3D models. It allows you to navigate, select, and manipulate objects in your scene.
- Navigation: Use the middle mouse button (MMB) to rotate, shift + MMB to pan, and scroll wheel to zoom.
- Selection: Right-click to select objects, shift + right-click to select multiple objects.
- Manipulation: Use the toolbar on the left or shortcuts (G for move, R for rotate, S for scale) to transform objects.
Outliner
The Outliner provides a hierarchical view of all objects in your scene. It allows you to:
- Select Objects: Click on an object name to select it.
- Hide/Show Objects: Click the eye icon to toggle visibility.
- Organize: Drag and drop objects to organize them into collections.
Properties Editor
The Properties Editor contains various tabs, each representing different settings and properties for the selected object or scene:
- Render: Settings for rendering the scene.
- Output: Settings for outputting the rendered image or animation.
- View Layer: Settings for view layers and passes.
- Scene: General scene settings.
- World: Settings for the world environment.
- Object: Settings for the selected object.
- Modifiers: Add and configure modifiers for the selected object.
- Material: Settings for the object's material.
- Texture: Settings for textures applied to the object.
- Particle: Settings for particle systems.
- Physics: Settings for physics simulations.
Timeline
The Timeline is used for animation. It shows keyframes and allows you to control playback.
- Play/Pause: Use the play button or spacebar to start/stop playback.
- Keyframes: Add keyframes by pressing I and selecting the property to keyframe.
- Scrubbing: Click and drag the playhead to scrub through the timeline.
Customizing the Interface
Blender's interface is highly customizable. You can adjust the layout to suit your workflow:
- Resizing Areas: Click and drag the borders between areas to resize them.
- Splitting/Joining Areas: Right-click on the border between areas to split or join them.
- Creating Custom Workspaces: Arrange the editors as needed and save the layout as a new workspace.
Practical Example
Let's create a simple custom workspace for modeling:
- Start with the Default Layout: Open Blender and ensure you are in the Layout workspace.
- Split the 3D Viewport: Right-click on the border of the 3D Viewport and select "Vertical Split". Drag to create a new area.
- Change the New Area to the Outliner: Click on the editor type selector (top-left corner of the new area) and select "Outliner".
- Resize the Areas: Adjust the size of the 3D Viewport and Outliner to your preference.
- Save the Workspace: Click the "+" button next to the workspace tabs and name your new workspace "Custom Modeling".
Exercises
Exercise 1: Navigating the Interface
- Open Blender and switch to the "Modeling" workspace.
- Use the 3D Viewport to navigate around the default cube.
- Select the cube in the Outliner.
- Change the cube's material in the Properties Editor.
Solution
- Open Blender and click on the "Modeling" tab at the top.
- In the 3D Viewport, use the middle mouse button to rotate, shift + MMB to pan, and scroll wheel to zoom.
- In the Outliner, click on "Cube" to select it.
- In the Properties Editor, click on the "Material" tab (sphere icon) and change the material settings.
Exercise 2: Customizing the Interface
- Create a new workspace called "Custom Animation".
- Split the 3D Viewport horizontally and change the new area to the Timeline.
- Resize the areas to your preference.
- Save the workspace.
Solution
- Click the "+" button next to the workspace tabs and name the new workspace "Custom Animation".
- Right-click on the border of the 3D Viewport and select "Horizontal Split". Drag to create a new area.
- Click on the editor type selector in the new area and select "Timeline".
- Adjust the size of the 3D Viewport and Timeline to your preference.
- The workspace is automatically saved.
Conclusion
Understanding the Blender interface is essential for efficient workflow and productivity. By familiarizing yourself with the different workspaces, editors, and customization options, you can tailor Blender to suit your specific needs and preferences. In the next section, we will dive into basic navigation and controls, building on the foundation we've established here.
Blender Course: From Beginner to Advanced
Module 1: Introduction to Blender
- Getting Started with Blender
- Understanding the Blender Interface
- Basic Navigation and Controls
- Creating and Saving Projects
Module 2: Basic Modeling Techniques
- Introduction to 3D Modeling
- Working with Primitives
- Basic Transformations: Move, Rotate, Scale
- Using Modifiers
Module 3: Advanced Modeling Techniques
Module 4: Materials and Texturing
Module 5: Lighting and Rendering
- Introduction to Lighting
- Types of Lights in Blender
- Setting Up a Scene for Rendering
- Using the Render Engine
